Urology Care at Great Falls Clinic
At Great Falls Clinic, our board-certified urologists provide comprehensive care and specialized treatment for patients of all ages, from children with congenital conditions to seniors with age-related concerns. Using the latest diagnostic technology and treatment approaches, our experts deliver personalized care for both adult and pediatric urology in a comfortable, supportive environment.
Expert Treatment for All Urological Health Concerns
Women’s Urinary Health
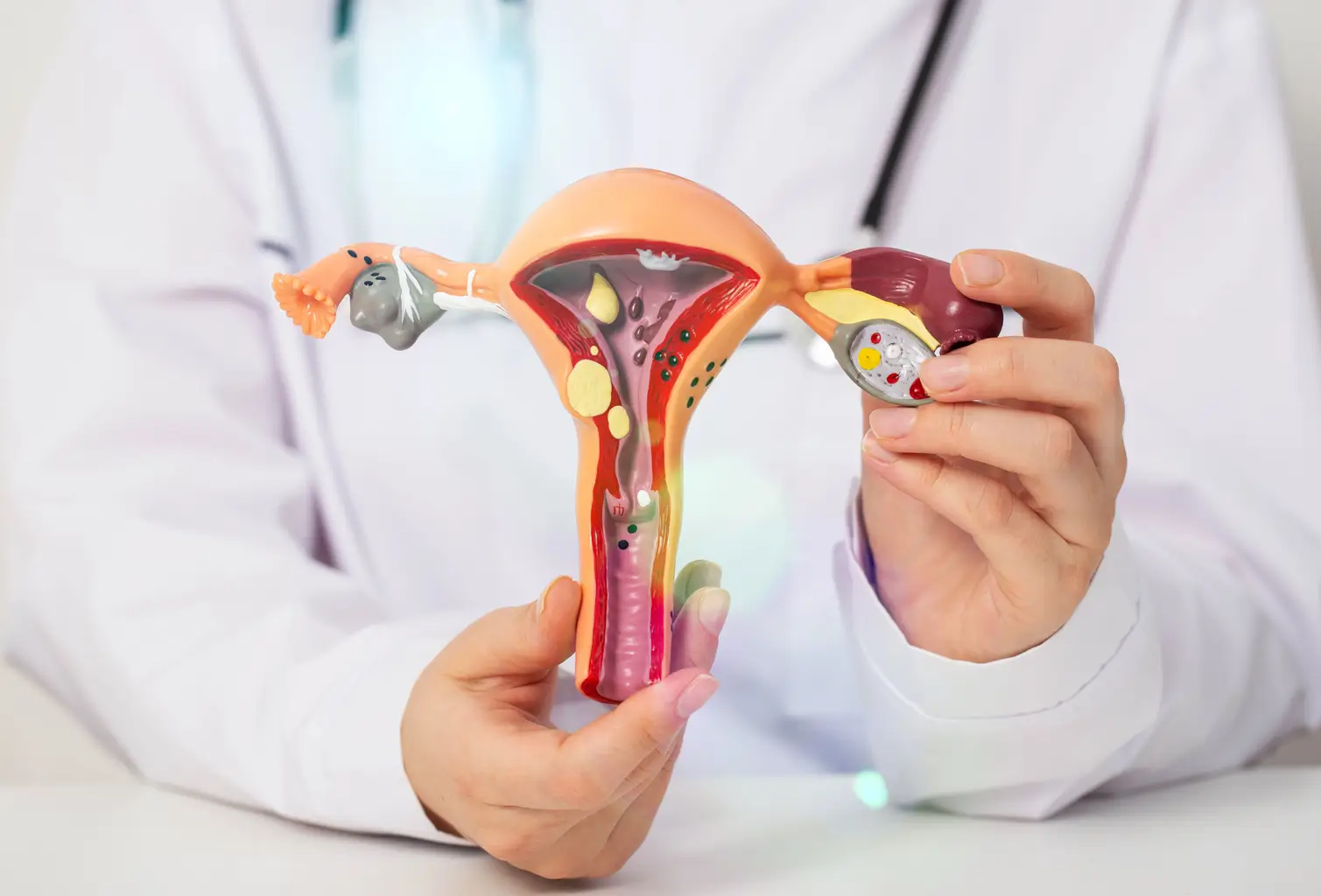
Female Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the muscles and ligaments supporting a woman’s pelvic organs weaken, allowing these organs to drop from their normal position and put pressure on the vaginal walls. Common symptoms include vaginal pain, lower back pain, a “lump” in the vagina, pain during intercourse, vaginal bleeding, urine leakage, constipation, and difficulty voiding.
Several organs may be affected by pelvic organ prolapse:
Bladder prolapse (cystocele): This is the most common type of pelvic organ prolapse, which occurs when the bladder pushes down on the vaginal wall, creating a bulge.
Urethral prolapse (urethrocele): This condition often accompanies bladder prolapse and happens when the urethra pushes on the vaginal wall, potentially causing urinary symptoms.
Rectum prolapse (rectocele): This type of prolapse occurs when the rectum pushes on the back wall of the vagina, which may lead to difficulties with bowel movements.
Uterine prolapse: This condition occurs when the uterus descends through the vaginal opening, sometimes becoming visible outside the body in severe cases.
Vaginal vault prolapse: This happens when the ceiling of the vagina drops down, which is commonly seen after hysterectomy due to weakened supporting structures.
Small bowel prolapse (enterocele): This type of prolapse develops when the small bowel pushes through the vaginal wall, often creating a bulge in the upper posterior vagina.
Urogenital fistula: A urogenital fistula is an abnormal opening between the urinary system (bladder, ureters, or urethra) and the vagina or rectum. An estimated 2 million women worldwide live with unrepaired urogenital fistulas. A key concern is that if left untreated, urogenital fistulas result in constant vaginal leakage of urine—fistulas between the rectum and vagina cause fecal leakage from the vagina.
Urogenital fistulas can result from pelvic surgery, foreign bodies, trauma, infection, or pelvic radiation. Diagnosis requires a medical history, vaginal examination, imaging, and sometimes cystoscopy. Since non-surgical approaches rarely work, most cases need surgical repair (typically vaginal, though laparoscopic or robotic options exist), followed by 2-3 weeks with a catheter during recovery.
Men’s Urological Health
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Advanced treatments for an enlarged prostate include medication therapy, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical options to relieve troublesome urinary symptoms. BPH treatment options include medications (alpha-blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors) to improve symptoms, minimally invasive procedures (TUMT, TUNA, Rezūm, and UroLift) for moderate cases, and surgical interventions (TURP, laser therapies, prostatectomy, and robotic procedures) when necessary—all personalized to your specific condition and prostate characteristics.
Erectile Dysfunction: Personalized treatment plans can address physical and psychological factors, from oral medications to advanced therapeutic options. Erectile dysfunction care includes a multi-tiered approach: first-line treatments, including oral medications to enhance blood flow, lifestyle modifications, management of underlying conditions, and psychological counseling when appropriate; advanced therapies such as vacuum devices, penile injections, intraurethral suppositories, and shock wave therapy for those needing additional intervention; and surgical options including penile implants, vascular repairs, and reconstructive procedures for cases resistant to other treatments.
Vasectomy: Safe and effective permanent contraception for men seeking a reliable birth control solution. Vasectomy procedures include traditional techniques (conventional vasectomy with small incisions) and advanced approaches (no-scalpel vasectomy, minimally invasive methods) performed under local anesthesia. The procedure involves careful isolation of the vas deferens, precise blocking methods (removal of segments, cauterization, and fascial interposition), and minimal recovery time with success rates exceeding 99%—all conducted with attention to patient comfort, minimal complications, and thorough pre-procedure counseling about the permanent nature of this contraceptive choice.
Pediatric Urology
Specialized care and advanced treatments for urological conditions in children, including congenital anomalies, functional disorders, and reconstructive procedures tailored to growing bodies. Pediatric urology management options include diagnostic approaches (prenatal ultrasound, voiding cystourethrogram, and urodynamic studies) for early detection, medical therapies (antibiotic prophylaxis, anticholinergics, and behavioral modifications) for functional disorders, and surgical interventions (hypospadias repair, orchiopexy, pyeloplasty, and minimally invasive techniques) when necessary—all adapted to your child’s specific condition, developmental stage, and long-term urological health.
Urologic Oncology
Bladder Cancer: Comprehensive approaches for detection and treatment of this urological malignancy, encompassing diagnostic protocols, preservative strategies, and definitive interventions based on cancer stage and grade. Bladder cancer management options include detection methods (cystoscopy, urine cytology, and biomarker tests) for early diagnosis, treatment approaches (intravesical immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted molecular therapies) for non-invasive disease, and surgical interventions (TURBT, radical cystectomy with urinary diversion, and nerve-sparing techniques) when indicated—all personalized to your specific tumor characteristics, overall health status, and quality of life considerations.
Prostate Cancer: Advanced detection and treatment options include screening protocols, targeted therapies, and precision surgical approaches to effectively manage this common male cancer. Prostate cancer management options include screening methods (PSA testing, digital rectal exams, and multiparametric MRI) for early detection, treatment approaches (active surveillance, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy) for various cancer stages, and surgical interventions (radical prostatectomy, nerve-sparing techniques, and robotic-assisted procedures) when necessary—all tailored to your specific diagnosis, cancer characteristics, and personal health factors.\
Kidney Cancer: State-of-the-art detection and treatment protocols for renal cell carcinoma and other kidney malignancies. Management includes precise staging (TNM classification, nuclear grading), surgical interventions (robotic/laparoscopic partial or radical nephrectomy), systemic therapies (targeted agents, immunotherapy, combination approaches), and multidisciplinary care throughout surveillance—all personalized to your specific cancer type, stage, genetic profile, and performance status.
Urinary Health
Incontinence: Effective solutions for both male and female urinary leakage may include conservative approaches (pelvic floor training, bladder retraining, dietary modifications), medications (anticholinergics, beta-3 agonists, alpha-blockers, topical estrogen), minimally invasive procedures (bulking agents, Botox, nerve stimulation), and surgical interventions (slings, artificial sphincters, bladder neck suspension) tailored to the severity and type of incontinence.
Hematuria: Comprehensive evaluation and treatment for blood in the urine, which may include diagnostic approaches (urinalysis, imaging studies, cystoscopy), medical management (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, stone dissolution therapy), and interventional procedures (lithotripsy, tumor resection, vascular embolization) when necessary—all customized to identify and address the underlying cause, whether it’s infection, stones, trauma, tumors, or other conditions affecting the urinary tract.
Urethral Strictures: Comprehensive treatment approaches for narrowing of the urethral passage in males and females, including diagnostic methods, conservative management, and reconstructive techniques to restore normal urinary flow. Urethral stricture management options include diagnostic procedures (retrograde urethrogram, cystoscopy, and uroflowmetry) for accurate assessment, minimally invasive treatments (urethral dilation, internal urethrotomy, and stent placement) for short strictures, and reconstructive surgeries (urethroplasty, graft techniques, and staged repairs) for complex or recurrent cases—all customized to your specific stricture location, length, and underlying etiology to achieve optimal long-term outcomes.
Neurogenic Bladder: Comprehensive management approaches for bladder dysfunction caused by neurological conditions, encompassing diagnostic evaluations, conservative therapies, and advanced interventions to improve quality of life. Neurogenic bladder treatment options include assessment tools (urodynamic testing, cystoscopy, and video urodynamics) for precise diagnosis, conservative strategies (intermittent catheterization, timed voiding, and pharmacological management with anticholinergics, beta-3 agonists, and alpha-blockers) for symptom control, and interventional approaches (botulinum toxin injections, sacral neuromodulation, and bladder augmentation) when necessary—all customized to your specific neurological condition, bladder function parameters, and overall health status.
Urinary Tract Infections: Prompt treatment and preventive strategies for acute and recurrent infections, including precise diagnostics with targeted antibiotic therapy, pain management, and hydration for acute infections. For recurrent cases, preventive strategies may be implemented, including prophylactic antibiotics, estrogen therapy, cranberry/D-mannose supplements, probiotics, and personalized lifestyle modifications, with specialized approaches for complicated infections, including anatomical correction when necessary.
Voiding Dysfunction: Specialized care for difficulties with urination, including frequent urination, incomplete emptying, and overactive bladder. Following a comprehensive assessment, behavioral therapies (double voiding, scheduled urination, fluid management), medications (alpha-blockers, anticholinergics, beta-3 agonists), and advanced interventions (catheterization, Botox, neuromodulation) when needed. Surgical options range from minimally invasive urethral procedures to more complex reconstructive surgeries for severe cases.
Kidney Health
Kidney Stones: Complete care for urinary tract calculi, from acute pain management to stone removal and prevention strategies. Treatment approaches include medical management (pain control, alpha-blockers, and hydration therapy), minimally invasive procedures (shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy with laser lithotripsy, and percutaneous nephrolithotomy), and metabolic evaluation with personalized prevention plans—all tailored to your specific stone composition, location, and overall health status.
Kidney (Renal) Mass: Comprehensive evaluation and management of renal masses, from incidental findings to complex lesions. Assessment includes advanced imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI), diagnostic procedures (renal biopsy when indicated), and treatment options ranging from active surveillance for small benign masses to nephron-sparing approaches (partial nephrectomy, ablative therapies) for indeterminate or complex lesions—all customized to your specific mass characteristics, renal function, and health profile.
The Path to Urology Health Starts With Us
When you choose our Urology Clinic in Great Falls, MT, you gain a dedicated partner in your urological health. Our patient-centered approach means we take time to understand your concerns, explain conditions clearly, and develop treatment plans that fit your lifestyle and preferences.
Our urologists collaborate closely with other specialists across the entire Great Falls Clinic and Hospital to provide integrated care for complex conditions, ensuring you receive comprehensive treatment from a team that communicates effectively about your needs.
Schedule Your Consultation
Don’t let urological concerns affect your quality of life. Our compassionate team is ready to help you address these sensitive issues with dignity and expert care.
Call (406) 205-1915 today to schedule your consultation with one of our urology specialists.
